Developing the most efficient solution to remove micropollutants from wastewater in an innovative approach
Micropollution is a raising concern in most of developed countries and somewhat untreated issue from many municipal wastewater treatment plants. In recent years, an increasing focus on the environmental state of many waterbodies have been noticed along with the development and testing of various treatment solutions.
We wanted to demonstrate the effect of splitting the ozone dose into two due to various reasons in full scale:
- By injecting ozone directly into the biological tanks in an aeration phase, the biological sludge would also experience removal of micropollutants. In Denmark, most of the municipal sludge ends to the farms. Therefore removing micropollutants decreases the later run-off and general spread of the pollution to the environment.
- Having bromide in water can give severe problems regarding tertiary ozonation. However, by splitting the ozone dose in two and thereby lowering the tertiary ozone doses, the risk of forming the cancerogenic substances like bromate is much lower. Simply because the ozone dose initially attacks the micropollution i.e., pharmaceuticals in biological tank.
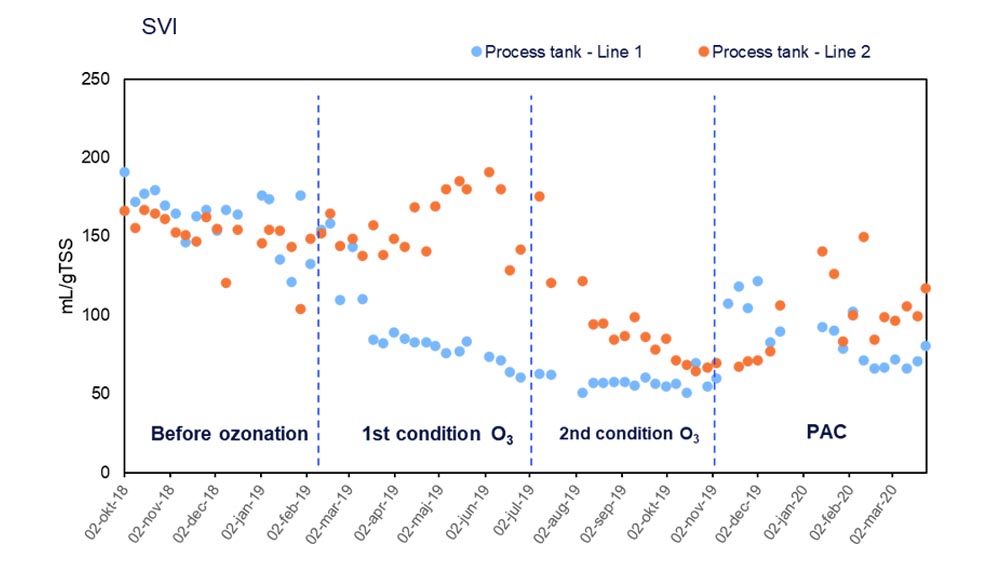
- Furthermore, ozonation was believed to lower the Sludge Volume Index and thereby give a higher capacity in a wastewater treatment plant simple because ozone would reduce the filamentous bacteria.
Application of multiple point ozone injection
SUEZ solutions use oxidizing power of ozone that increases the reduction of oxidizable micropollutants.
We have demonstrated the most effective solution to remove micropollutants from wastewater by splitting ozone dose in to two points, in secondary - Bio3 option - and tertiary treatment - Oxyblue product. SUEZ Bio3 option is biological tanks naming dependent: as examples, Biofor Bio3 for biofilters, Ultrafor Bio3 for ultrafiltration membrane reactors.
Through our extensive full-scale study in Brædstrup wastewater treatment plant we could conclude several major benefits and water quality improvements:
*Predicted No Effect Concentration
Effective removal of all tested micropollutants from wastewater and no bromide in discharge water
The experimental demonstration lasted 1,5 years at Brædstrup municipal wastewater treatment plant. Brædstrup was suited for this purpose, because the plant has two separate treatment lines that split after pre-treatment. A baseline analysis of the plant found no major differences between the performance (average of 55% removal of the 36 pharmaceuticals tested) and microbial composition of the two lines.
About the test program:
- Approx. 36 (mainly) pharmaceuticals
- Water and solid phase analysis
- Conventional parameters measured and observed.
- Microbial composition analysed (DNA)
- E. coli, antibiotic resistant bacteria + genes
- Ecotoxicological
- + more…
Two different tests with ozonation each lasting for minimum 110 days:
- Low dose in biological tanks, high tertiary ozone dose
- High dose in biological tanks, low tertiary ozone dose
Both tests had the same summed dosage.
Results micro pollutant removal in water
All compounds above Predicted No Effect Concentration in inlet are all below in outlet, after two points of ozonation. The second line at Brædstrup wastewater treatment plant served as reference throughout the test period. Only shown are those compounds above PNEC in both inlet and outlet of reference line (those that possess a potential to the environment).
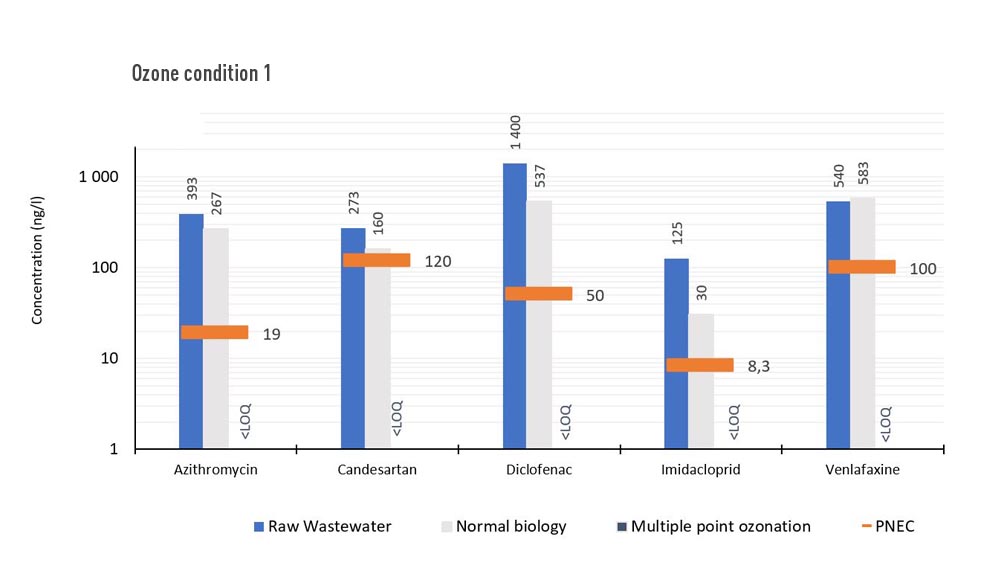
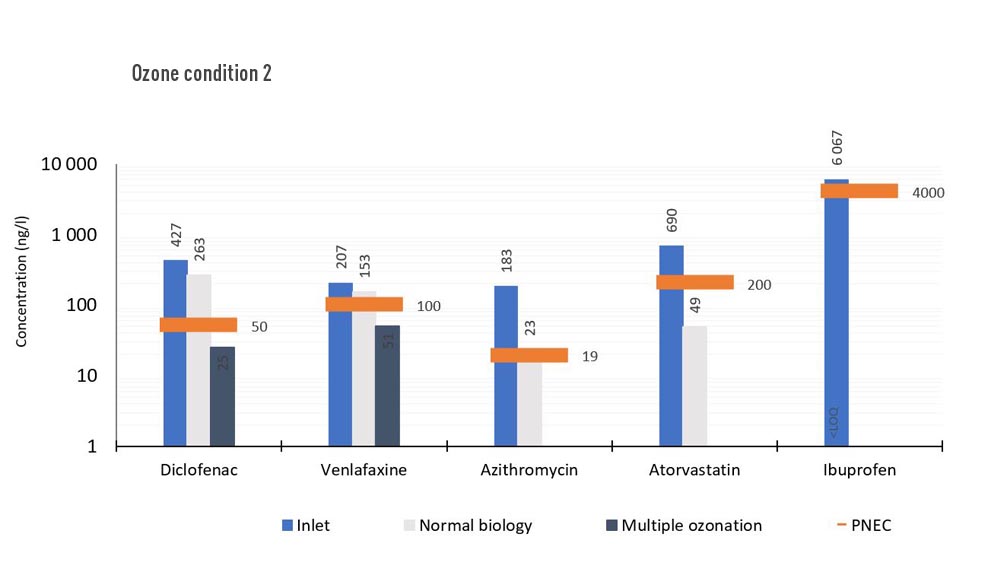
Baseline – Normal biology – 55 % in water
1. Ozone campaign – 93 % in water – all below PNEC - 38 % total removal in sludge
2. Ozone campaign – 86 % in water – all below PNEC - 43 % total removal in sludge
Results Sludge Volume Index
Application of Powder Activated Carbon (PAC)
We have demonstrated an innovative approach to upgrade the existing wastewater treatment plant to remove micropollutants from wastewater by integrated PAC injection into biological tank.
Through our extensive full-scale study in Brædstrup wastewater treatment plant we could conclude up to 30% improvement in the reduction of adsorbable micropollutants compared to activated sludge without PAC.
Two different tests with PAC injection each lasting for minimum 40 days.
Contact our expert

If you have any questions or would like to know more, send email to:


